Search Earthquake Catalog
online search by time window, area, magnitude, and more
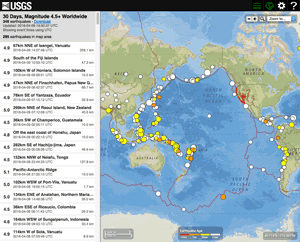
Significant Earthquakes, Past 30 days
5.2
6.3
6.8
4.9
4.5
5.1
4.9
5.7
6.2
7.4
6.4
7.1
6.6
5.2
6.3
6.8
4.9
4.5
5.1
4.9
5.7
6.2
7.4
6.4
7.1
6.6
Earthquake Hazards Program
The USGS monitors and reports on earthquakes, assesses earthquake impacts and hazards, and conducts targeted research on the causes and effects of earthquakes. We undertake these activities as part of the larger National Earthquake Hazards Reduction Program (NEHRP), a four-agency partnership established by Congress.