Portal:Ecology
| |
|
|
Ecology
|
|
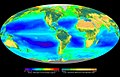
Ecology (from Ancient Greek οἶκος (oîkos) 'house' and -λογία (-logía) 'study of') is the natural science of the relationships among living organisms, including humans, and their physical environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere levels. Ecology overlaps with the closely related sciences of biogeography, evolutionary biology, genetics, ethology, and natural history. Ecology is a branch of biology, and is the study of abundance, biomass, and distribution of organisms in the context of the environment. It encompasses life processes, interactions, and adaptations; movement of materials and energy through living communities; successional development of ecosystems; cooperation, competition, and predation within and between species; and patterns of biodiversity and its effect on ecosystem processes. Ecology has practical applications in conservation biology, wetland management, natural resource management (agroecology, agriculture, forestry, agroforestry, fisheries, mining, tourism), urban planning (urban ecology), community health, economics, basic and applied science, and human social interaction (human ecology). The word ecology (German: Ökologie) was coined in 1866 by the German scientist Ernst Haeckel. The science of ecology as we know it today began with a group of American botanists in the 1890s. Evolutionary concepts relating to adaptation and natural selection are cornerstones of modern ecological theory. Ecosystems are dynamically interacting systems of organisms, the communities they make up, and the non-living (abiotic) components of their environment. Ecosystem processes, such as primary production, nutrient cycling, and niche construction, regulate the flux of energy and matter through an environment. Ecosystems have biophysical feedback mechanisms that moderate processes acting on living (biotic) and abiotic components of the planet. Ecosystems sustain life-supporting functions and provide ecosystem services like biomass production (food, fuel, fiber, and medicine), the regulation of climate, global biogeochemical cycles, water filtration, soil formation, erosion control, flood protection, and many other natural features of scientific, historical, economic, or intrinsic value. (Full article...) Selected article - The San Francisco Estuary together with the Sacramento–San Joaquin River Delta represents a highly altered ecosystem. The region has been heavily re-engineered to accommodate the needs of water delivery, shipping, agriculture, and most recently, suburban development. These needs have wrought direct changes in the movement of water and the nature of the landscape, and indirect changes from the introduction of non-native species. New species have altered the architecture of the food web as surely as levees have altered the landscape of islands and channels that form the complex system known as the Delta. This article deals particularly with the ecology of the low salinity zone (LSZ) of the estuary. Reconstructing a historic food web for the LSZ is difficult for a number of reasons. First, there is no clear record of the species that historically have occupied the estuary. Second, the San Francisco Estuary and Delta have been in geologic and hydrologic transition for most of their 10,000 year history, and so describing the "natural" condition of the estuary is much like "hitting a moving target". Climate change, hydrologic engineering, shifting water needs, and newly introduced species will continue to alter the food web configuration of the estuary. This model provides a snapshot of the current state, with notes about recent changes or species introductions that have altered the configuration of the food web. Understanding the dynamics of the current food web may prove useful for restoration efforts to improve the functioning and species diversity of the estuary. (Full article...)Selected image - Credit: User:Nhobgood Ocellaris clownfish often live symbiotically with the Heteractis magnifica sea anemone, using them for shelter and protection.
General imagesThe following are images from various ecology-related articles on Wikipedia.
Related WikiProjectsThings you can do
Entries here consist of Good and Featured articles, which meet a core set of high editorial standards.
 In zoology, automimicry, Browerian mimicry, or intraspecific mimicry, is a form of mimicry in which the same species of animal is imitated. There are two different forms. In one form, first described by Lincoln Brower in 1967, weakly-defended members of a species with warning coloration are parasitic on more strongly-defended members of their species, mimicking them to provide the negative reinforcement learning required for warning signals to function. The mechanism, analogous to Batesian mimicry, is found in insects such as the monarch butterfly. (Full article...)Selected biography - Leonty Grigoryevich Ramensky (Russian: Лео́нтий Григо́рьевич Ра́менский; June 16 [O.S. June 6] 1884 – January 27, 1953) was a plant ecologist who conceived several important ideas that were overlooked in the West and later ’re-invented’ by western scientists. He lived in the Russian Empire and later the Soviet Union. He graduated from the Petrograd University in 1916 and obtained a Ph.D. in biology in 1935. From 1911 to 1928 he worked in the Research Institute of the Voronezh Gouvernement (now Voronezh State University) and from 1928 in the State Grassland Institute (later All-union Scientific Research Institute of Forages dedicated to V.R.Williams). Ramensky was a proponent of the view that biotic communities consist of species behaving individualistically (much like Henry Gleason in the U.S.A.). This was in strong contrast to the prevailing view of communities as super-organisms, held by the powerful V.N.Sukachov and his consorts (much like Frederic Clements in the U.S.A.). Hence, Ramensky was marginalized within the Russian scientific community and was only posthumously rehabilitated by Russian ecologists. Much later, the significance of his ideas was discovered by ecologists in the West. (Full article...)Did you know (auto-generated)
Selected quote -
Ecology news
Additional News Highlights
Selected publication -Ecotropica is a biannual, peer-reviewed international scientific journal covering all aspects of tropical ecology. Papers reflect results of original research (major papers, short communications) or review important fields in tropical ecology. (Full article...) Related portalsMore did you know -Related articlesAssociated WikimediaThe following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
Web resources
Discover Wikipedia using portals |