Deep Space Expedition Alpha (DSE-Alpha)
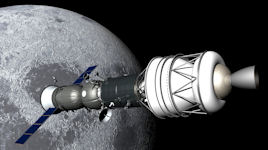 The Deep Space Expedition Alpha (DSE-Alpha), would take place via a modified Soyuz-TMA capsule. According to what was previously reported by Space Adventures, the first of the two 150 million dollar "tickets" would have already been sold to a future space tourist. According to Kostenko the changes to be made to the capsule to support the astronauts during the flight around the Moon are rather "standard", and it will take only two or three years, starting from the sale of the second tourist seat, to complete the project and prepare the mission.
The Deep Space Expedition Alpha (DSE-Alpha), would take place via a modified Soyuz-TMA capsule. According to what was previously reported by Space Adventures, the first of the two 150 million dollar "tickets" would have already been sold to a future space tourist. According to Kostenko the changes to be made to the capsule to support the astronauts during the flight around the Moon are rather "standard", and it will take only two or three years, starting from the sale of the second tourist seat, to complete the project and prepare the mission.The circumlunar tourist flight being developed by the private company Space Adventures will have its own scientific mission, and could also host a subsatellite to be inserted into the lunar orbit. According to Sergei Kostenko, the representative of the company's Russian office, the scientific mission has not yet been planned but it will certainly be planned in the future, and one of the possibilities could be the deployment of a lunar probe.
The changes will concern the increase of the living space available to the three crew members, the commander and the two tourists, through the use of a small additional module to make the stay on board more comfortable for the duration of the mission, more than one week. Changes to the landing system will also be necessary, given the greater speed of return than normal Soyuz flights, and the radiation protection system.
The Constellation program was announced by George W. Bush at the beginning of the 21st century. This is a kind of rethinking of the Apollo program at the present stage, based on new technologies, including the technology of the shuttle. It was supposed to create a new ship, called Orion, and two new rockets - Ares I and Ares V. It all reminded of the Apollo expedition, only more and better - four people on the Moon, a long (up to a month) stay on the surface. However, this program was closed by Barack Obama in 2010. The main argument for closing is that this program offers nothing fundamentally new.
In Russia, almost simultaneously with the announcement of Constellation in the United States, they also recalled long-distance missions. There were ideas for using existing equipment (Soyuz spacecraft, Soyuz and Proton launch vehicle, upper stage D) for the lunar landing expedition. The scheme was cumbersome, with a huge number of launches (about ten). It is clear that with the help of existing rockets of the middle and heavy class it is impossible to assemble the lunar expedition without docking. Nevertheless, the work was carried out, and even there were preliminary studies of the Russian lunar landing module.
Perhaps the most real idea at the time was to send space tourists to fly around the moon. Two launches using the Soyuz and Proton launch vehicles, launching the modified Soyuz lunar spacecraft and the D block, docking, acceleration using D block and flying around the moon. The scheme in terms of ballistics and the masses was complicated. One of the problems is reliability. Accordingly, before the flight of the tourist, unmanned launches would be required, which immediately greatly increased the price of the ticket.
In 2005, the concept of a tourist flight around the Moon appeared under the name DSE-Alpha: two tourists and a mission commander. The originator of the expedition is Space Adventures, which is very successful in organizing space tourism. At the moment, one of the two available tickets for the price of 150 million dollars has been sold, and we know the details of the missions presented at the conference in May 2014.
From the technical side, the idea seemed to have a solid foundation. Equipment in the form of a ship and transfer stage already exist. The Space Adventures idea is based on the Soyuz ship as part of a mission from 1967-1970 under the designation Zond 4-8 (and some unsuccessful missions that were marked otherwise - a total of 14 vehicles). It is extremely interesting that they would be the great losers of the first space race of the 1960. Soyuz, and the transfer block Block D were originally designed for the moon mission. Both survived the programs for which they were created and new applications were found for them. In August 1969, Zond 7 went on a lunar flight. The mission was model-based. If the crew were on board, they would take a textbook flight with a controlled return to the atmosphere. For the first time in the history of the program she would come back alive and in good condition. It was the only lunar flight of Soyuz in history, which was a complete success.
To do this, the Soyuz would be joined by a new module - “logistics module”. It is put into orbit by an additional rocket. In this module - everything that is necessary for a cruise to the Moon: fuel, water supplies and products, an additional navigation system and all other things that the customer may wish for - a wealthy thrill-seeker. This trip will take six days. They flew up, looked at the reverse side of the moon, saw through a telescope the glands thrown on the satellite by the Americans, and back home.
Constellation Services International, Inc. (CSI) was an "early stage" orbital services company that is currently focused on cargo resupply to low Earth orbit (LEO) and satellite retrieval and repair. CSI is developing and patenting an innovative method to resupply space platforms in LEO using existing technology that called LEO Express SM Space Cargo Services.
CSI first presented a concept for a low-cost, near-term trip around the Moon on July 17, 2004 at the "Return to the Moon Conference V" as the Lunar ExpressSM Space Transportation System. CSI's approach could enable a human mission to the Moon in 2-3 years. More importantly, by re-using an existing Soyuz that is first used in a mission to ISS, CSI may have discovered a way to make a human trip to the Moon commercially viable. "Low Cost" and "Human Trip to the Moon" are not mutually exclusive terms. Because of this, CSI is pondering some interesting, and unusual, possibilities.
- Would some wealthy individual be willing to pay (enough) to provide a premier space adventure -- first an initial weeklong stay at ISS, and then a weeklong trip around the Moon like Apollo 8 or 10? What is it worth to be the first private citizen, ever, to see an "Earth Rise"?
- Would another nation be willing to pay for the second seat, and to send their first citizen ever around the Moon?
- What are the branding opportunities?
CSI’s Lunar ExpressSM system for a near-term trip around the Moon is based on existing flight-proven technology and could be available in 3 years or less. Using this system, the grand prize winner of the FreeSpaceShot.com game could take a 6-day trip around the Moon, after first visiting the International Space Station. CSI, a commercial orbital services firm, is leading a team of aerospace companies with world-class expertise in ISS operations to develop the reliable, economical, and flexible LEO ExpressSM ISS cargo resupply system with initial service planned in 2009. CSI has offices in Laguna Woods, CA, and Alexandria, VA. "LEO Express" and "Lunar Express" are trademarks and service marks of Constellation Services International, Inc.
Constellation Services International, Inc. (CSI) congratulated Space Shot, Inc. on the January 15, 2007 announcement of FreeSpaceShot.com, which provides students and other ordinary people the opportunity to win a trip around the Moon by playing a skill-based game on the internet. “Private spaceflight innovation is not just a matter of technology, but of coming up with ways to allow every person to participate," stated CSI's CEO, Charles Miller. "CSI is pleased to support Space Shot’s efforts to create new ways to increase the interest and participation of younger generations. FreeSpaceShot.com offers everyone with skill and persistence the opportunity to fly in space."
All of this turned into vaporware.
|
NEWSLETTER
|
| Join the GlobalSecurity.org mailing list |
|
|
|

