| 1. | Thread: Dining Philosophers | | |
| 2. | Synchronizing on another object | |  |
| 3. | Operations that may seem safe are not, when threads are present | |  |
| 4. | Synchronizing blocks instead of entire methods | |  |
| 5. | Boolean lock | |  |
| 6. | Static synchronized block | |  |
| 7. | Thread notify | |  |
| 8. | Thread deadlock | | 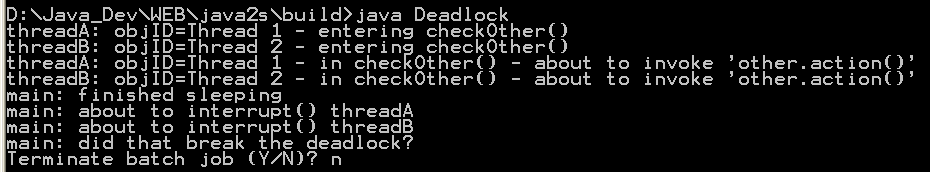 |
| 9. | Synchronize method | | 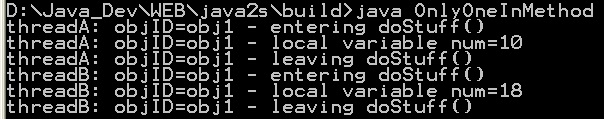 |
|
| 10. | Threads join | | 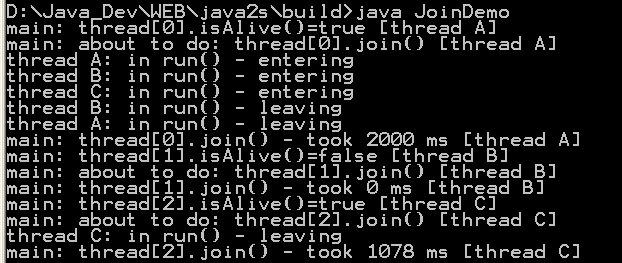 |
| 11. | Static synchronize | | 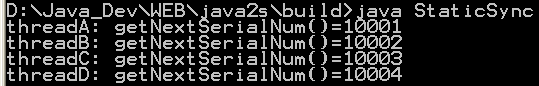 |
| 12. | No synchronize | |  |
| 13. | Thread synchronization | |  |
| 14. | Synchronized Block demo | | 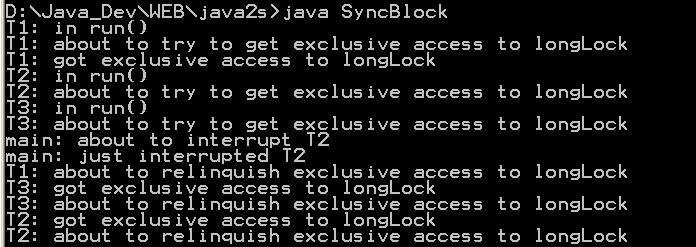 |
| 15. | Interruptible Synchronized Block | | 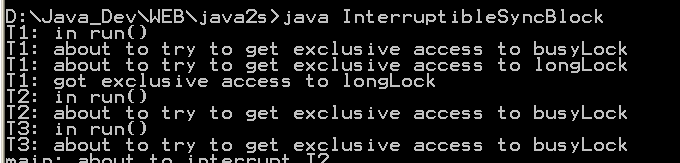 |
| 16. | Signaling | | 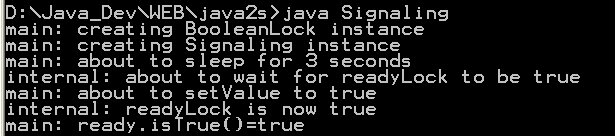 |
| 17. | Simple Object FIFO | | 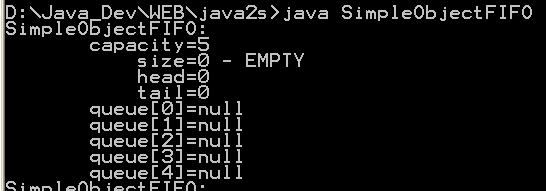 |
| 18. | Object FIFO | |  |
| 19. | Byte FIFO | |  |
| 20. | Daemon Lock | | |
| 21. | Determining If the Current Thread Is Holding a Synchronized Lock | | |
| 22. | Handle concurrent read/write: use synchronized to lock the data | | |
| 23. | Lock for read and write | | |
| 24. | Read Write Lock | | |
| 25. | Coordinates threads for multi-threaded operations | | |
| 26. | A reader-writer lock from "Java Threads" by Scott Oak and Henry Wong. | | |
| 27. | Invoke a series of runnables as closely to synchronously as possible | | |
| 28. | This program shows how multiple threads can safely access a data structure, using synchronized methods | | |
| 29. | This program shows data corruption when multiple threads access a data structure. | | |
| 30. | Stores a single object for the producer/consumer pattern and takes care of thread synchronization. | | |
| 31. | The BooleanLock class provides a useful encapsulation of a boolean variable that is easily and safely accessed from multiple theads. | | |