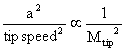VII. Production of Thrust with a Propeller
A. Overview of propeller performance
Each propeller blade is a rotating airfoil which produces lift and drag, and because of a (complex helical) trailing vortex system has an induced upwash and an induced downwash.

Figure 7.1 Cessna Skyhawk single engine propeller plane (Cessna, 2000)

Figure 7.2 Schematic of propeller (McCormick, 1979)
The two quantities of interest are the thrust (T) and the torque (Q). We can write expressions for these for a small radial element (dr) on one of the blades:
![]()
![]()
where
![]() and
and ![]()
It is possible to integrate the relationships as a function of r with the appropriate lift and drag coefficients for the local airfoil shape, but determining the induced upwash (ai) is difficult because of the complex helical nature of the trailing vortex system. In order to learn about the details of propeller design, it is necessary to do this. However, for our purposes, we can learn a about the overall performance features using the integral momentum theorem, some further approximations called “actuator disk theory”, and dimensional analysis.
NASA Glenn has a nice explanation of propeller thrust - GO! |

Figure 7.3 The V-22 Osprey utilizes tiltrotor technology (Boeing, 2000)
B. Application of the Integral Momentum Theorem to Propellers
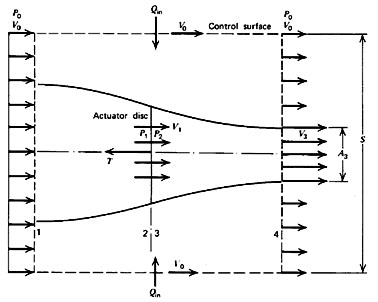
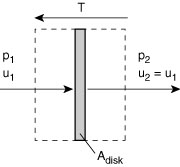
Figure 7.4 Control volume for analysis of a propeller (McCormick, 1979)
The control volume shown in Figure 7.3 has been drawn far enough from the device so that the pressure is everywhere equal to a constant. This is not required, but it makes it more convenient to apply the integral momentum theorem. We will also assume that the flow outside of the propeller streamtube does not have any change in total pressure. Then since the flow is steady we apply:
![]()
Since the pressure forces everywhere are balanced, then the only force on the control volume is due to the change in momentum flux across its boundaries. Thus by inspection, we can say that
![]()
Or we can arrive at the same result in a step-by-step manner as we did for the jet engine example in Section II:
![]()

Note that the last term is identically equal to zero by conservation of mass. If the mass flow in and out of the propeller streamtube are the same (as we have defined), then the net mass flux into the rest of the control volume must also be zero.
So we have:
![]()
as we reasoned before.
The power expended is equal to the power imparted to the fluid which is the change in kinetic energy of the flow as it passes through the propeller

The propulsive power is the rate at which useful work is done which is the thrust multiplied by the flight velocity
![]()
The propulsive efficiency is then the ratio of these two:

Which is the same expression as we arrived at before for the jet engine (as you might have expected).
C. Actuator Disk Theory
To understand more about the performance of propellers, and to relate this performance to simple design parameters, we will apply actuator disk theory. We model the flow through the propeller as shown in Figure 7.4 and make the following assumptions: