- Workplace Statistics
- Time Management Statistics
- Employee Wellness Statistics
- Employment Discrimination Statistics
- Employee Recognition Statistics
- Employee Referral Statistics
- Workplace Violence Statistics
- Gamification Statistics
- Employee Feedback Statistics
- Agile Statistics
- Productivity Statistics
- Meeting Statistics
- Cell Phones At Work Statistics
- Social Media At Work Statistics
- Workplace Injury Statistics
- Workplace Stress Statistics
- Leadership Statistics
- Workplace Collaboration Statistics
- Job Satisfaction Statistics
- Paid Holiday Statistics
- Communication In The Workplace Statistics
- Wasting Time At Work Statistics
- 4-day Workweek Statistics
Research Summary. You’ve likely heard before that Americans are now more productive than they’ve ever been. While this is partially true, it’s worth dissecting what this means in a modern context. What is the current state of productivity, and where are we headed? According to our extensive research:
-
The average employee is productive for 2 hours and 53 minutes a day. That’s only 31% of the average 8-hour workday.
-
At least 41% of workers say that stress leads them to be less productive.
-
On average, workers are 13% more productive when working from home, and overall worker productivity in the U.S. has increased by 5% since the start of the pandemic.
-
Employees spend up to 32% of their time on Facebook, costing employers $28 billion each year.
-
It takes an average of 23 minutes and 15 seconds to refocus on a task after a distraction.
-
The average employee is distracted every 3 minutes.
For further analysis, we broke down the data in the following ways:
Employee | Employer | Top Problems | Over Time

General Employee Productivity Statistics
Of course, no employee or company is 100% equal when it comes to productivity. In the grand scheme, certain factors can make some employees more productive than others. Here are some insights our research uncovered:
-
Engaged employees are 21% more productive.
In fact, high employee engagement is a huge plus, as these teams also experience a 41% reduction in absenteeism, 59% less turnover, and 28% less internal theft.
-
Though the average employee is productive for 60% of their workday, office employees are only productive for 31% of their workday.
For the average employee, that equates to around 4.8 hours of productivity per day. However, that number is 2 hours and 53 minutes for office employees, or only 12.5 hours per week.
-
Freelance workers are productive for up to 87% of their workday.
When assuming that a freelancer is working five days per week, the fact that they clock an average of 36 hours per week means that they’re productive for at least 7 hours per day.

Self-Reported Employee Productivity Statistics
Though daily employee productivity might seem surprisingly low, what do the employees think about their productivity? Here’s are their thoughts:
-
Only 7% of employees feel productive in the workplace.
Which correlated with the fact that employees are only productive for an average of 2 hours and 53 minutes per day. Likely, most employees feel unproductive because they spend the majority of their workday distracted.
-
66% of employees believe they’d be more productive if they worked from home.
For the most part, this conclusion is reached because 76% of employees want fewer interruptions from colleagues and other distractions, 70% want to reduce stress from commuting, and 69% want to avoid office politics.
-
46% of employees feel as though digital tools make them more productive.
In fact, only 7% of workers believe that technology has decreased their productivity. According to these employees, the most important digital tools they use are email (61% say it’s very important) and the internet (54% say it’s very important).

Employer Productivity Statistics
Now that we know what employees think about their productivity, it’s worth addressing how employers view the situation. Are they doing anything to address the problem or simply adding to it? Our research shows that:
-
Productive companies have 30-50% higher operating margins than their less productive counterparts.
Research has shown that the best companies are up to 40% more productive than other companies. This means that productivity is even more important than overall efficiency.
-
To improve productivity, 76% of employees believe using company-provided wearable tech to track employees would help.
However, many employees are understandably concerned about how employers will use their fitness and health information.
-
Twenty-four billion hours are wasted each year as the result of unproductive meetings.
And at least 37% of employees consider unproductive meetings to be the biggest cost to their organization. It’s no wonder; 24 billion is a considerable amount of productive work hours being lost.
-
The average corporate employee spends 4 hours preparing for and attending meetings per week.
With 54% of employees reporting that their meetings last over 30 min. And, 35% of employees agree that the 2-5 hours wasted on meetings each week leaves them with no benefits.
Top Productivity Problems
To address the current state of employee productivity, it’s important to understand the main causes of decreased productivity. After all, some distractions are far more detrimental than others! Here are the facts:
-
Multitasking can reduce productivity by up to 40%.
In fact, even the idea of multitasking is almost entirely a myth, as 98% of the population can’t or has a very hard time multitasking. With that in mind, it’s no surprise that trying to multitask can hurt productivity.
-
Less than 25% of employees prefer to work in teams.
And this could impact productivity, as, within the past five years, employees report that the amount of time they spend in meetings, on phone calls, or answering emails has increased by 50% and takes up at least 80% of their time.
-
The average employee spends up to 32% of their time on social media, or 2.35 hours daily.
One of the main culprits is Facebook, which has cost employers a staggering $28 billion in productivity losses annually.
-
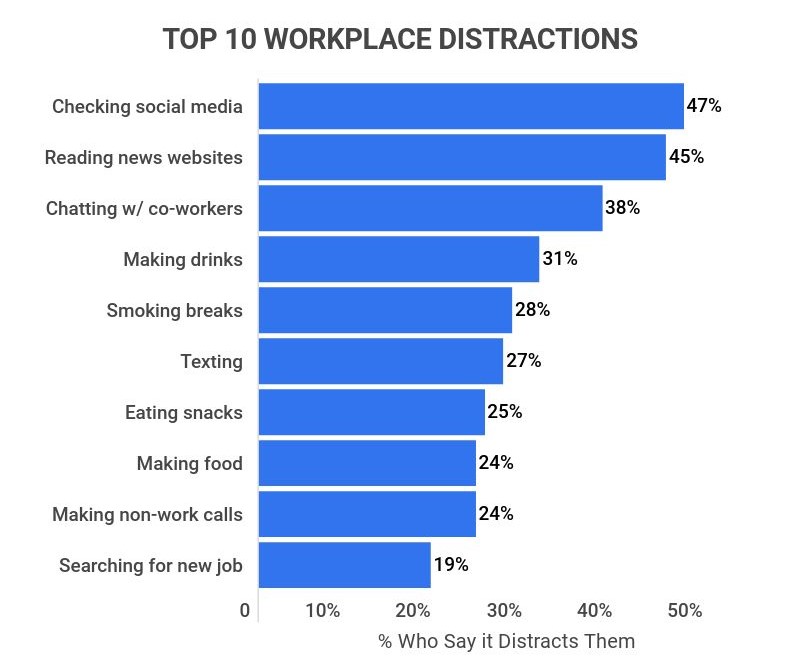
Checking social media is also the most common and prominent distraction, with 47% of employees checking it in the workplace.
Other common workplace distractions include reading news websites (45% of employees), discussing out-of-work activities with colleagues (38% of employees), making hot drinks (31% of employees), and smoking breaks (28% of employees).
-
80% of employees feel stressed because of ineffective company communication.
And this number only seems to be growing, as it increased by 30% from 2018-2019. In fact, communication barriers within companies cost an average of $26,000 per year.
-
70% of employees admit to feeling distracted on the job.
With at least 16% stating that they’re almost always distracted, and 54% feeling as though they aren’t performing as well as they should.
-
It takes an average of 23 minutes and 15 seconds to refocus on a task after a distraction.
And that’s bad news, seeing as the average employee is disrupted every three minutes and five seconds. No wonder daily productivity is so low.
Employee Productivity Over Time Statistics
While, on the one hand, productivity has increased over time, technology has also provided greater distractions. Regardless, Americans now are more productive than they’ve ever been. With that in mind, where is productivity headed? Here are the facts:
-
Productivity has increased by 61.8% from 1979 to 2020.
However, it’s interesting that this increase in productivity has not been met with similar wage growth, as wages have only increased by 17.5%. Further, most of this growth can be attributed to technology, as employees are actually more distracted than ever.
-
Productivity Management Software Market is expected to experience a CAGR of 14.2% from 2021 to 2028.
Currently, this technology-based productivity market is worth $42.62 billion. By 2028 this number is expected to reach $119.69 billion.
-
Microsoft 365 (otherwise known as Microsoft Office) is the most common productivity software used.
This includes things like Word, Excel, Powerpoint, and Outlook. Microsoft 365 is also cloud-based, making it easy to keep track of, move, and store data.
Productivity Statistics FAQ
-
How productive is the average American worker?
The average American worker is only productive for 2 hours and 53 minutes a day. That’s just 31% of the average 8-hour workday. Employees aren’t oblivious to this either, as a meager 7% feel productive in the workplace.
However, this is not to say that productivity is at an all-time low or has decreased over time. On the contrary, productivity as a whole has increased by 61.8%.
-
Productivity is measured by drawing comparisons between the number of goods and services produced with the inputs used in production. This process is most commonly and accurately carried out by the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS).
Therefore, in particular, labor productivity is the ratio of the goods and services output to the hours devoted to creating that output.
-
What is a good productivity percentage?
A good productivity percentage is somewhere between 70-75%. This means that employees spend 70% or more of their time working and 25% or less of their time taking breaks. This allows for maximum profit without risking burnout or a poor work-life balance.
As you may have noticed, though, this isn’t the norm. Most Americans are only productive for a maximum of 60% of the time, with office workers down to only 31% of the time, while freelance workers are productive for a staggering 87% of the time.
-
What does a productivity expectation of 75% mean?
A productivity expectation of 75% means that the employee isn’t burning themselves out by always working at full capacity. This way, if demands increase temporarily, they can respond efficiently without going over their limit.
For example, an employee working at 75% will have vacations, small breaks, and unscheduled portions of the day. Doing so will give the employee more energy when it’s time to work and lead to a more healthy and more steady productivity rate overall.
-
What is a productivity analysis?
A productivity analysis is a process that collects data in order to determine how to improve productivity. In general, employers will use a productivity analysis to identify weak spots and strong spots among their employees.
For example, these studies can help determine the following:
-
Valuable vs. non-valuable work
-
Identify cost reduction opportunities
-
Outline more efficient ways to perform the tasks.
-
Assess the quality of current operations
Afterward, employers can then use these insights to create goals, eliminate non-valuable work, and cut costs. All of which are extremely crucial forms of streamlining for any business.
-
-
How do you calculate productivity increase?
Calculating productivity increase is relatively simple but does take a few steps. Let’s say a company implemented new policies to improve production in 2021. They could calculate how their productivity has changed using the following steps:
-
Calculate the current productivity with this equation: Number of units completed ÷ hours spent to complete units (e.g., in 2021, there were six units completed ÷ 3 hours = two units produced per hour)
-
Calculate previous productivity with the same method: in 2020, there were six units ÷ 4 hours = 1.5 units produced per hour
-
Subrated the old rate from the new rate: 2 – 1.5 = 0.5 production improvement
-
Calculate the percentage difference: Production improvement ÷ Old production figure x 100 (e.g. 0.5 ÷ 1.5 = 0.33 x 100 = 33%)
In this situation, making improvements cause production to increase by 33%.
-
Conclusion
Americans are simultaneously more productive and more distracted than we’ve ever been when it comes to productivity. While productivity has increased by 61.8% since 1979, the truth is that the average American is only productive for 2 hours and 53 minutes a day.
Likely, technology plays an important role on both fronts. For example, productivity software like Microsoft 365 and others have made it easier than ever to streamline the workplace, and the productivity management software market is expected to continue growing by at least 14.2% through 2028.
However, 47% of employees also admit to checking social media in the workplace, with time spent on social media amounting to an average of 2 hours and 35 minutes daily (or 32% of the workday).
With that in mind, it’s clear that there’s an issue of distraction within the workplace. And, this issue is one which employers aren’t exactly sure to solve. However, there are promising signs amongst freelance and remote workers, who are productive for 87% of their workday and 13% more productive overall.
Sources:
-
Forbes. “Employee Engagement And Employee Productivity Aren’t The Same Thing — Here’s How To Boost Both.” Accessed on October 25th, 2021.
-
Vouchercloud. “How Many Productive Hours in a Work Day? Just 2 Hours, 23 Minutes…” Accessed on October 25th, 2021.
-
Yahoo!Finance. “Freelancers work more hours than the average American does.” Accessed on October 25th, 2021.
-
Forbes. “Report: Only 7% Of Workers Feel Productive During Regular Work Hours.” Accessed on October 25th, 2021.
-
Pew Research Center. “Technology’s Impact on Workers.” Accessed on October 25th, 2021.
-
HBR. “Great Companies Obsess Over Productivity, Not Efficiency.” Accessed on October 25th, 2021.
-
CITYA.M. “Employers want to use wearable tech to track the health, sleep, fitness and productivity of the office.” Accessed on October 25th, 2021.
-
Doodle. “The State of Meetings 2019.” Accessed on October 25th, 2021.
-
BOOQED. “Minutes (Wasted) of Meeting: 50 Shocking Meeting Statistics.” Accessed on October 25th, 2021.
-
Forbes. “Want To Be More Productive? Stop Multi-Tasking.” Accessed on October 25th, 2021.
-
Microsoft. “New survey explores the changing landscape of teamwork.” Accessed on October 25th, 2021.
-
ETCIO. “Employees spend over 32% of their time on social media daily for personal work: study.” Accessed on October 25th, 2021.
-
Marlin. “The Hidden Costs of Employee Miscommunication.” Accessed on October 25th, 2021.
-
Lifehack. “7 Most Common Distractions at Work (And How to Tackle Them).” Accessed on October 25th, 2021.
-
The Washington Post. “Work interruptions can cost you 6 hours a day. An efficiency expert explains how to avoid them.” Accessed on October 26th, 2021.
-
EPI. “The Productivity–Pay Gap.” Accessed on October 25th, 2021.
-
Grand View Research. “Productivity Management Software Market Report, 2021-2028.” Accessed on October 26th, 2021.
-
Techradar.pro. “Best productivity tools of 2021.” Accessed on October 26th, 2021.
- Workplace Statistics
- Time Management Statistics
- Employee Wellness Statistics
- Employment Discrimination Statistics
- Employee Recognition Statistics
- Employee Referral Statistics
- Workplace Violence Statistics
- Gamification Statistics
- Employee Feedback Statistics
- Agile Statistics
- Productivity Statistics
- Meeting Statistics
- Cell Phones At Work Statistics
- Social Media At Work Statistics
- Workplace Injury Statistics
- Workplace Stress Statistics
- Leadership Statistics
- Workplace Collaboration Statistics
- Job Satisfaction Statistics
- Paid Holiday Statistics
- Communication In The Workplace Statistics
- Wasting Time At Work Statistics
- 4-day Workweek Statistics






