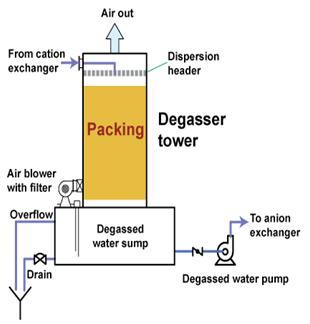
A degasser or degasifier is often used to remove dissolved carbon dioxide after cation exchange column. Degasser is an integral part of any demineralisation plant, where it is generally placed between cation and anion exchange units. It removes carbon dioxide, which is generated by dissociation of carbonic acid at cation outlet water. Degasser tower is made from either FRP or mild steel lined with rubber. Low air pressure is generated at the bottom of the tower that drives out carbon dioxide and degasser water is collected in a sump beneath the tower.

Degasser systems are available in ASME and IEI Good Engineering Practices
Degasser systems are available for flow rates of 7.5 m³/h to120 m³/h. We can design for bigger capacities based on client's requirement.
Applications: